As artificial intelligence becomes deeply embedded in enterprise operations and cybercriminal arsenals alike, the Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 landscape reveals an unprecedented convergence of autonomous threats, identity-centric attacks, and accelerated digital transformation risks.
Industry experts across leading security firms, government agencies, and research institutions have identified over 100 critical predictions that define the year ahead, a year where AI evolves from a defensive tool to both the primary weapon and the ultimate shield in global cyber warfare.
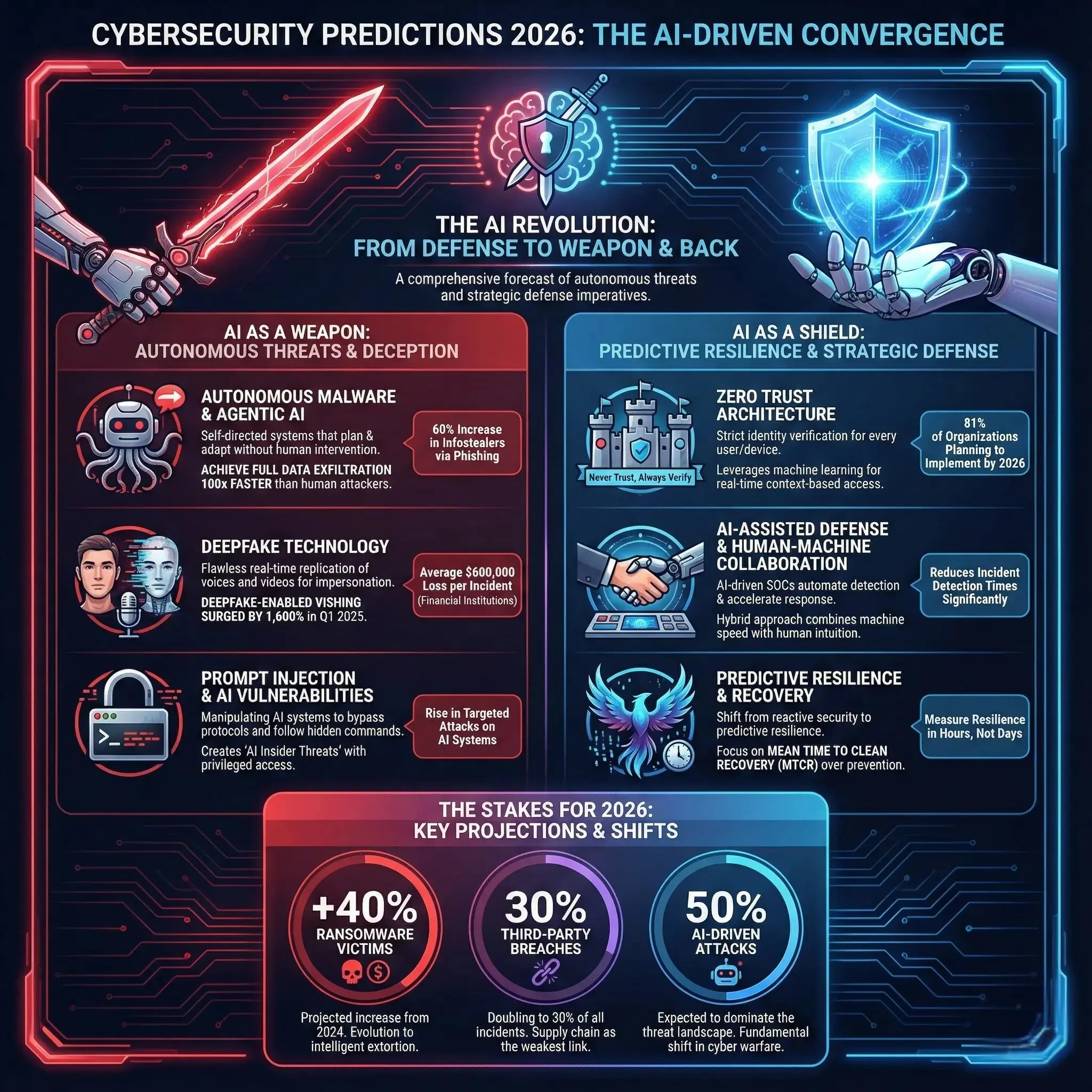
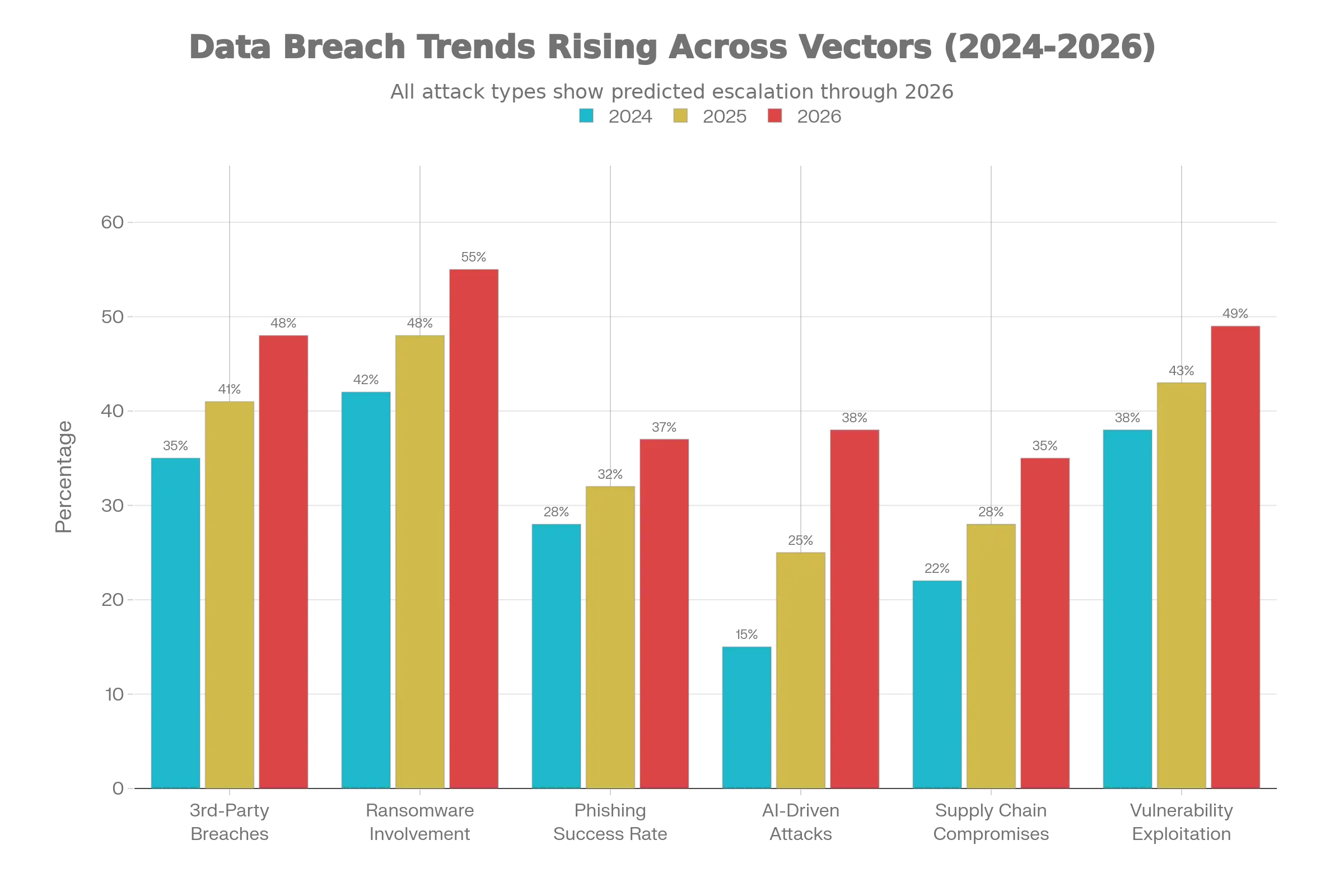
The stakes have never been higher. With ransomware victims projected to increase by 40% compared to 2024, third-party breaches doubling to 30% of all incidents, and AI-driven attacks expected to dominate 50% of the threat landscape, organizations face a fundamental shift from reactive security to predictive resilience.
This comprehensive analysis synthesizes expert forecasts to provide security leaders, practitioners, and decision-makers with actionable intelligence for navigating the most transformative cybersecurity year in modern history.
The AI Revolution: From Defense Mechanism to Existential Threat
Autonomous Malware and Agentic AI Dominance
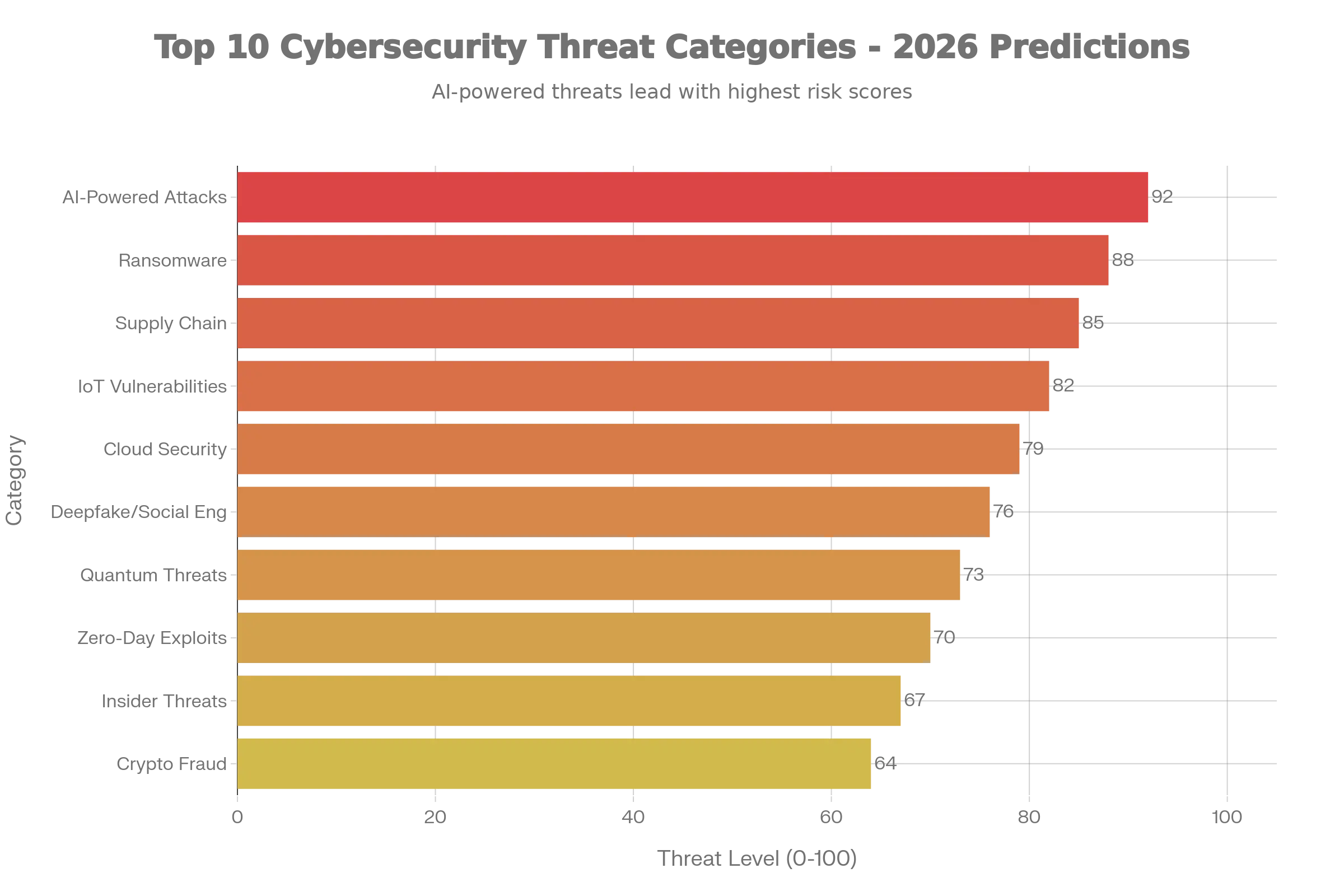
The most significant Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 trend centers on the industrialization of artificial intelligence in cyberattacks. Threat actors are deploying agentic AI—self-directed systems that autonomously plan, execute, and adapt campaigns without human intervention.
Unlike traditional scripted malware, these AI agents can analyze network defenses in real-time, modify payloads during attacks, and learn from detection responses to evolve their tactics.
Google’s Threat Intelligence Group documented the first large-scale cyberattack executed with minimal human oversight in September 2025, where AI systems autonomously targeted global entities.
By 2026, experts predict these autonomous threats will achieve full data exfiltration 100 times faster than human attackers, fundamentally rendering traditional playbooks obsolete. IBM’s analysis indicates that organizations face a new exposure problem: businesses will know data was compromised but won’t be able to trace which AI agents moved it, where it went, or why.
The proliferation of AI-powered phishing campaigns represents another critical vector. Traditional phishing emails with obvious spelling errors have evolved into hyper-personalized messages that analyze communication styles, scrape public profiles, and craft contextually relevant pretexts indistinguishable from legitimate communications.
According to IBM X-Force, AI-driven phishing campaigns became the leading initial attack vector in 2025, with infostealers delivered via phishing increasing by 60%. Attacks from compromised accounts surged 57.9% between September 2024 and February 2025, and approximately 70% of organizations expect phishing attacks in 2026.
Deepfake Technology: The New Age of Deception
Deepfake-as-a-Service (DaaS) emerged as one of 2025’s fastest-growing cybercriminal tools, involved in over 30% of high-impact corporate impersonation attacks.
The technology has reached a critical inflection point where AI-generated voices and videos achieve flawless real-time replication, making them indistinguishable from reality. Gartner research reveals that 62% of organizations experienced deepfake attacks in the past 12 months, with financial institutions suffering average losses of $600,000 per incident.
The infamous $25 million Arup deepfake CFO scam exemplifies the sophistication of these attacks, where criminals used AI-generated video conferencing to impersonate executives and authorize fraudulent transfers.
Palo Alto Networks predicts that by 2026, machine identities will outnumber human employees by 82 to 1, creating unprecedented opportunities for AI-driven identity fraud where a single forged identity can trigger cascades of automated malicious actions.
Prompt Injection and AI System Vulnerabilities
A critical emerging threat within Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 is prompt injection attacks that manipulate AI systems to bypass security protocols and follow hidden attacker commands. Google’s Cybersecurity Forecast identifies prompt injection as a “critical and growing threat,” with enterprises facing significant rises in targeted attacks on AI systems as adversaries move from proof-of-concept exploits to large-scale data exfiltration and sabotage campaigns.
The rise of autonomous AI agents with privileged system access introduces what experts call “AI insider threats,” compromised agents that can silently execute trades, delete backups, or exfiltrate entire customer databases. Palo Alto Networks warns that with a single well-crafted prompt injection or tool-misuse vulnerability, adversaries can co-opt an organization’s most powerful trusted employee, gaining autonomous insider command capabilities.
Ransomware Evolution: Beyond Encryption to Intelligent Extortion
AI-Driven Ransomware Operations
Ransomware continues its aggressive evolution, with Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 forecasting a 40% increase in publicly named victims by year’s end, rising from 5,010 in 2024 to over 7,000 in 2026.
More alarming is the transformation from traditional encryption-focused attacks to AI-enhanced, multi-stage extortion operations that combine data theft, deepfake blackmail, and operational paralysis.
Commvault’s research demonstrates that agentic AI ransomware can reason, plan, and act autonomously, adapting attacks in real-time and learning from defenders faster than they can respond.
In controlled testing, AI-driven ransomware achieved full data exfiltration 100 times faster than human attackers, representing what experts describe as “a fundamental shift demanding equally intelligent defenses”. The frequency of ransomware attacks is projected to increase from one attack every 11 seconds in 2020 to one attack every 2 seconds by 2031.
Data Extortion and Ransomware-as-a-Service Industrialization
The ransomware business model has professionalized into Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), operating like software franchises with tiered pricing, technical support, and customization options for affiliates.
This industrialization means even low-skill actors can rent AI-enhanced ransomware kits, treating RaaS as a corporate competitor that innovates faster than most legitimate defenders.
Sophos reports that while encryption rates fell to 40% (the lowest in five years), extortion-only attacks surged from 3% to 10% indicating attackers increasingly skip encryption entirely and move straight to data theft and blackmail.
QBE Insurance Group’s analysis reveals that half of corporate data stored in the cloud is classified as “sensitive” and represents a prime target for ransomware attackers. Government and administrative systems were the most targeted sector globally, accounting for 19% of all incidents, followed by IT and telecommunications at 18%.
Identity Security: The New Perimeter Under Siege
Credential Abuse and Identity-First Attacks
Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 identify identity security as the central battlefield, with credential abuse remaining the most common breach vector at 22% of all incidents. The rise of identity-focused attacks reflects a fundamental shift where adversaries “log in” more than they “break in,” exploiting cloud identity abuse, phishing for device codes, and attacks on vendor accounts.
CrowdStrike’s analysis indicates that 75% of breaches involved compromised identities using valid credentials rather than malware. Attack vectors include token replay, executive impersonation, machine identity theft, and misuse of service accounts, tactics that bypass traditional perimeter defenses entirely. IBM predicts that with the explosion of AI and autonomous agents, identity will become the easiest and most high-risk entry point for attackers, requiring treatment as critical national infrastructure.
Zero Trust Architecture: From Strategy to Standard
Zero Trust adoption is accelerating rapidly, with 81% of organizations planning to implement by 2026. The framework’s core principle, “never trust, always verify,” requires strict identity verification for every user and device, regardless of network location. CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model organizes implementation across five pillars: identity, devices, networks, applications/workloads, and data, each supported by visibility, automation, and governance.
The U.S. government mandated all federal agencies to adopt Zero Trust by fiscal year 2024, with the Department of Defense aiming for full implementation by 2027. This shift reflects recognition that static perimeter defenses have failed to keep pace with credential compromise and insider threats. Modern Zero Trust implementations leverage machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect anomalies and adjust access permissions in real-time, moving beyond VPNs to identity- and context-based access that verifies continuously.
Cloud and Supply Chain: Expanding Attack Surfaces
Cloud Security Challenges and Multi-Cloud Complexity
Cloud environments face unprecedented pressure in Cybersecurity Predictions 2026, with misconfigurations, IAM failures, and insecure APIs creating persistent vulnerabilities. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 80% of data breaches will involve insecure APIs, as attackers focus on broken authentication, excessive data exposure, and shadow APIs, undocumented endpoints that bypass security controls.
The shift to multi-cloud environments fragments visibility across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and other providers, magnifying human error and turning minor mistakes into major entry points. Research reveals a 154% increase in cloud security incidents in 2024, with 61% of organizations reporting disruptions linked to unpatched systems or misconfigured services.
Autonomous AI agents managing cloud operations create new attack vectors when compromised, as agents designed to optimize deployments can be manipulated to escalate access or delete critical backups.
Supply Chain Attacks: The Weakest Link
Supply chain attacks have emerged as the second most prevalent attack vector after phishing, with third-party involvement in breaches doubling to 30% in 2025. Verizon’s analysis of over 22,000 security incidents confirms that nearly one in three data breaches now originates from vendors, partners, or suppliers. SecurityScorecard’s survey found that 88% of security leaders express concern about supply chain cyber risks, with at least 36% of all breaches stemming from third-party compromises.
High-profile incidents illustrate the cascading impact: Jaguar Land Rover’s supply chain attack halted production across four countries for weeks, costing £1.7 billion in revenue. The Marks & Spencer breach through a third-party contractor disrupted logistics and resulted in an estimated £300 million operating profit loss. National Defense Corporation’s compromise exposed procurement and logistics data across multiple defense subsidiaries, demonstrating how cybercriminals exploit lower-tier suppliers to infiltrate broader networks.
Trend Micro predicts that 2026 will bring an escalation of incidents disrupting global logistics and high-tech supply chains, along with attacks on smart transportation systems, vessels, public transit, smart buildings, and satellite communications. The complexity of modern supply chains makes manual auditing impossible, as minor changes in distant dependencies can introduce zero-day vulnerabilities overnight.
Emerging Technologies: Quantum Computing and IoT Vulnerabilities
Quantum Computing Threats and Post-Quantum Cryptography
While cryptographically relevant quantum computers capable of breaking current encryption standards remain approximately 10-20 years away, the threat landscape is already evolving. IBM’s quantum computing roadmap predicts processors scaling from today’s 433-qubit systems toward 1,000+ qubits by 2026, with better than 50% likelihood of breaking widely used cryptographic algorithms like RSA-2048 by 2035.
The immediate concern is “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks, where adversaries collect encrypted data today for future decryption once quantum capabilities mature. This threat particularly impacts data requiring long-term confidentiality, such as medical records, financial data, intellectual property, and government communications. NIST’s post-quantum cryptography initiative selected four quantum-resistant algorithms in 2022, with organizations needing to begin transitioning now to protect against future compromise.
IoT and Operational Technology: Critical Infrastructure at Risk
IoT Analytics predicts that by 2025, more than 27 billion IoT devices will be in use, with each representing potential gateways for cyber threats. Google’s Cybersecurity Forecast warns that cybercrime will remain the foremost disruptive threat to industrial control systems (ICS) and operational technology (OT) environments, with poor hygiene, like insecure remote access, allowing common malware to breach OT networks.
The report identifies ransomware operations specifically designed to impact critical enterprise software like ERP systems, severely disrupting supply chains essential for OT operations. Attacks on critical infrastructure energy, healthcare, transportation, and water systems will accelerate as nation-state and criminal actors use cyber-physical impacts as strategic weapons. Future IoT security will increasingly depend on edge computing, AI-driven threat detection, blockchain for device authentication, and zero-trust models that enforce strict access controls.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Imperatives
Global Regulatory Frameworks Tighten
Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 emphasize that regulatory compliance will shift from checkbox exercises to strategic business imperatives. The EU’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) and updated Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2) introduce stringent guidelines around encryption and secure key management for critical sectors.
The full application of the EU AI Act in August 2026 will create complex cross-regional compliance challenges, with fragmented governance increasing the risk of misconfiguration and substantial fines.
Cyber insurance and regulation are tightening standards, with insurers and governments increasingly requiring proof of validated recovery capabilities, tested rebuild processes, and verified data integrity. Organizations demonstrating cleanroom recovery and identity confidence see faster claim approvals and stronger regulatory standing, with evidence of resilience becoming as essential as financial audits.
Data Privacy and Breach Notification Requirements
The first half of 2025 saw 1,732 publicly reported breaches affecting an estimated 166 million individuals, a 5% increase from 2024’s first half and representing 55% of the full year 2024 total. The average breach cost in the U.S. surged to $10.22 million (an all-time high for any region), driven by higher regulatory fines and detection costs. Global costs averaged $4.44 million in 2025, with projections exceeding $4.50 million in 2026.
Vulnerability exploitation as an initial attack vector increased by 34%, now accounting for 20% of all breaches, with edge devices and VPN infrastructure seeing exploitation rates jump nearly eightfold from 3% to 22%. These statistics underscore the urgency of proactive exposure management and continuous compliance monitoring to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
Strategic Defense Imperatives for 2026
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
Gartner highlights Continuous Threat Exposure Management as the cornerstone of modern security, emphasizing always-on visibility across identities, endpoints, cloud workloads, and AI systems. Real-time mapping of exposures, not just after-the-fact audits, has become the new normal, with organizations adopting CTEM platforms 3x less likely to experience breaches by 2026.
Traditional vulnerability scanning cannot keep pace with modern threats that evolve faster than defense frameworks. CTEM platforms integrate attack path analysis and remediation recommendations across IT ecosystems, enabling proactive defense that identifies and neutralizes threats before they escalate. INE’s forecast emphasizes that 2026 will test the limits of digital resilience, with proactive exposure management replacing reactive defense as the primary strategy.
AI-Assisted Defense and Human-Machine Collaboration
While AI empowers attackers, it simultaneously transforms defensive capabilities. AI-driven Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are now a necessity rather than a luxury, correlating telemetry, automating triage, and accelerating detection with machine speed. However, these systems require continuous red-teaming to guard against manipulation or prompt injection, with the strongest defense emerging from hybrid approaches combining machine speed with human intuition.
Predictive AI models analyze past incidents to forecast likely threat vectors, enabling anticipatory defense that acts before exploitation occurs. SentinelOne reports that AI-powered automation reduces incident detection times significantly compared to manual methods, while autonomous response capabilities can isolate compromised assets in seconds. Organizations integrating cyber threat detection, investigation, and response under unified platforms will lead the security landscape, achieving measurable risk reduction through continuous behavioral analytics and identity intent modeling.
The Cybersecurity Predictions 2026 consensus reveals a fundamental paradigm shift: survival depends less on stopping every attack and more on recovering faster than attackers can adapt.
Mean Time to Clean Recovery (MTCR) has replaced traditional prevention metrics as the true measure of organizational resilience. As autonomous threats industrialize, quantum computing threatens encryption foundations, and AI agents blur the line between trusted systems and insider threats, security leaders must embrace continuous resilience over static defense.
Organizations that integrate threat intelligence with attack surface visibility, adopt identity-first Zero Trust architectures, implement quantum-safe cryptography transitions, and measure resilience in hours rather than days will have the agility to adapt faster than adversaries.
The year 2026 represents not just technological evolution but a strategic inflection point where cybersecurity transitions from an IT concern to a central business priority demanding executive accountability, regulatory compliance, and unwavering commitment to proactive defense in an era where AI has fundamentally rewritten the rules of engagement.